For Etica Funds, the Impact Report represents a fundamental tool to transparentlyreport the impact of its investments in reference to the Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations. By measuring and reporting these impacts transparently, we are able to give tangible shape to our vision, allowing us to pursue our mission and confirm our identity.
The impact generated by investments in the mutual funds managed by Etica Funds is based on two strategic levers: the selection of securities based on ESG criteria, implemented through the proprietary ESG methodology EticApproach®, and continuous stewardship. Thanks to our selection activity, for 25 years our funds have exclusively invested in businesses and countries characterised by their commitment to environmental, social and governance issues. This selection process is further supported by stewardship with the corporate bodies of the companies in the portfolio, including activities such as consistent dialogue and the exercise of voting rights, aimed at promoting increasingly responsible practices.
The Impact report 2025: the main results
The impact assessment explores a number of specific long-term strategic environmental and social areas of impact, using the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as a reference for the selected1 impact indicators. This report focuses on the following Sustainable Development Goals:

The impact data refer to the reference market (MSCI World ESG Universal Net Total Return as of 31/12/2024). For more information on the methodology, please refer to page 16 of the report.
The thematic areas of impact covered in this report, corresponding to major environmental and social challenges for the planet and aligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), are:
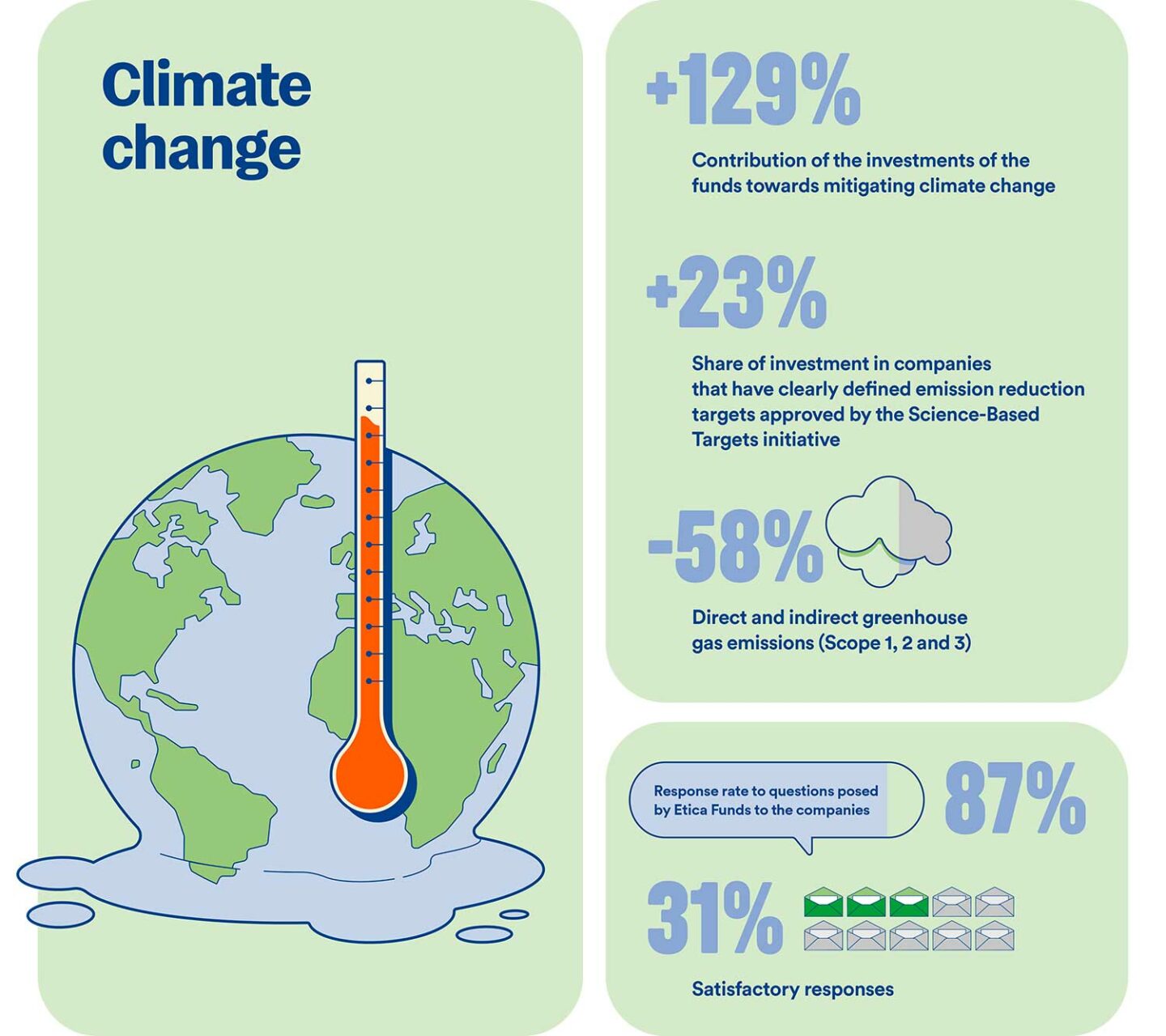
-
A company case study - Shimizu Corporation
Founded in 1804, the Shimizu Corporation is a long-standing Japanese construction and engineering firm that has adopted a pioneering approach to environmental sustainability. The company’s climate strategy is encapsulated in its vision, “SHIMIZU Beyond Zero 2050”, which commits to ensuring that its operating activities and the buildings it designs and constructs are carbon neutral by 2050. In 2024 the company set itself a number of particularly ambitious targets: reduce CO₂ emissions by 62% at its work sites, by 56% at its offices and by 54% in its building designs, compared to 1990 levels. To achieve these results, Shimizu has adopted innovation solutions such as the use of electric, bio-fuel and synthetic fuel powered machinery, as well as digital tools to monitor emissions and calculate the carbon content of materials. One emblematic example is the company’s head office in Tokyo, designed to be one of the least-emitting buildings in the world thanks to radiant systems, solar panels, smart lighting, and automatically adjustable window shades. Two of the most recent innovations are the Hydro Q-BiC system, which produces and stores hydrogen from solar energy, and DAC Coating, a concrete coating able to absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere. These initiatives demonstrate how Shimizu is driving the transformation of the construction sector towards a more sustainable model, making a tangible and measurable impact in the fight against climate change.

-
A company case study - Essilor Luxottica
EssilorLuxottica is a Franco-Italian multinational founded in 2018 through the merger of Essilor (France) and Luxottica (Italy). The group is a global leader in the design, production and sale of ophthalmic lenses, optical devices, corrective eyeglasses and sunglasses. In 2021 the company adopted a sustainability policy structured over five strategic pillars: carbon reduction, circularity, product access, inclusion, and business ethics. Specifically, with regard to circularity, EssilorLuxottica integrates eco-design principles into its products right from the design and development stage, with the aim of optimising the use of raw materials and prioritising the use of non-fossil based materials. The company has committed to adopting these eco-design principles into all of its product innovation processes by 2025. At the same time, it is making efforts to strengthen its capacity for internal recycling, extend the useful life of its products and develop circular services for customers, such as recycling programmes for used glasses. In 2024, over 40% of the company’s new collections were produced using materials with a low environmental impact. In the EMEA region, over 20,000 lenses were produced using over 4 tonnes of recycled nylon fibre. At a global level, the company has recovered and reused over 95 tonnes of nylon scraps from its internal production processes. EssilorLuxottica also translates its commitment to protecting biodiversity into action by pursuing environmental restoration projects in the regions in which it operates. For example, since 2020 the company has been implementing a 30-hectare reforestation project in Agordo, an area badly affected by Storm Vaia in 2018 and where Luxottica’s main manufacturing site is situated. The project involves removing and recovering the affected biomass to produce electricity for use in the production plant, obtaining FSC certification for the site, and constructing a forestry road to allow for its sustainable management.

-
A company case study - Boston Scientific Corporation
Boston Scientific Corporation is a US multinational that specialises in the development, production and sale of advanced biomedical devices. Its technological solutions span a broad range of treatment areas, including cardiology, neuromodulation, oncology, urology and gynaecology. The company is a pioneer in several fields of medical innovation: it is known for having developed the first controlled drug-eluting stent, which allows the active ingredient to be administered precisely in the areas where it is needed most, and for introducing a minimally invasive implantable defibrillator, which has significantly improved the effectiveness and comfort of life-saving treatments. For over twenty years Boston Scientific has promoted the “Close the Gap” initiative, aimed at improving equal access to healthcare in the communities it serves. The goal of the project is to remove the economic and systemic barriers that prevent access to care, taking action in the device development stage and during distribution. In the research phase, the company focuses on the main health risks for the most vulnerable categories of society. For example, in the United States it has helped to identify cardiovascular and neurological conditions that are particularly widespread among Hispanic and African-American communities, guiding the development of more targeted and effective solutions. As regards distribution, Boston Scientific has adopted a care access policy which includes administrative support and help with the reimbursement process. The aim is to ensure that bureaucratic barriers do not compromise access to treatment. One important example of this is the work carried out in 2024 to support health authorities in South-East Asia, aimed at guaranteeing the reimbursement of medical devices to treat heart arrhythmia conditions. Finally, the company continues to renew its commitment to clinical innovation, investing significant resources into research and development. In 2024 alone, Boston Scientific allocated over 1 billion dollars to R&D projects globally, with the aim of offering patients increasingly safe, effective and personalised treatments.

-
A company case study - Obayashi Corp
Obayashi Corporation is one of Japan’s leading construction companies, numbering among the top five operators in the sector at national level. Founded in Osaka in 1892, the company operates in Japan and internationally, with a strong presence in South-East Asia, Australia and the Middle East. Obayashi has adopted an integrated sustainability strategy, structured into material topics such as the energy efficiency of buildings, workers’ health and safety, and the reduction of environmental impact, setting out long-term goals for 2050 with intermediate targets for 2030 and 2040. From an environmental standpoint, the company is committed to reducing its emissions and constructing highly energy-efficient buildings, focusing in particular on the promotion of ZEB (Zero Energy Buildings). Obayashi has set itself the target of reducing Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 46% and Scope 3 emissions by 27% by 2030, compared to 2019. To achieve these goals, the company has improved the efficiency of its operations, introducing alternative fuels to replace diesel, renewing its vehicle fleet with latest generation models, including electric vehicles, and promoting the use of low carbon materials to replace traditional concrete. One tangible example of the company’s innovation is the introduction of “Clean-Crete”, a type of concrete with a carbon footprint that is 80% smaller that conventional concrete, obtained through the use of residues from blast furnace steel production. Obayashi’s environmental commitment also extends to biodiversity: the company was one of the first early adopters of the recommendations of the TNFD (Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures), committing to transparently report the impacts of its activities on nature.
Discover the Impact of Etica Funds’ Sub-Funds
This is a marketing communication.
Marketing communication by Etica SGR S.p.A. Investors should only enter into an investment transaction after fully understanding its overall characteristics and the level of exposure to the related risks, by carefully reading the KID and the Prospectus of the individual funds, which – together with information on sustainability aspects pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2019/2088 – are available on the website www.eticasgr.com. The recipients of this message assume full and sole responsibility for the use of the information contained in this communication and for any investment decisions made on the basis of it, as any use of this communication to support investment decisions is not permitted and is entirely at the investor’s own risk.


